how does a rotating retarder polarimeter work|polarimetry solar physics : tv shopping Rotating polarizer and rotating retarder plate polarimeters are widely used in high-resolution polarimetry, for example in remote sensing, fiber optic measurements and biomedics; as a . webConsiste no desbloqueio de matrícula no sistema acadêmico após a apreciação do colegiado do curso. Portanto, a REMATRÍCULA é um procedimento destinado ao estudante que está com a matrícula BLOQUEADA. A rematrícula deverá ser solicitada dentro do prazo estabelecido no Calendário Acadêmico em vigência. Documentos necessários:
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 19 de jul. de 2021 · 当虚拟机内存大于或等于物理机内存时会发生什么?真的会发生内存交换吗?
A computer-controlled Mueller matrix polarimeter with dual rotating retarders is described. Bulk properties of optical materials are determined by controlling the input-polarization state and measuring the output-polarization state.polarizer: optical element that produces polarized light from unpolarized input light linear, circular, or in general elliptical polarizer, depending on type of transmitted polarization linear polarizers .Rotating polarizer and rotating retarder plate polarimeters are widely used in high-resolution polarimetry, for example in remote sensing, fiber optic measurements and biomedics; as a .
The polarimetric engine of these instruments is often a dual rotating retarder (DRR). For low-error Mm extractions to be achieved, the retardance should be on the order of .
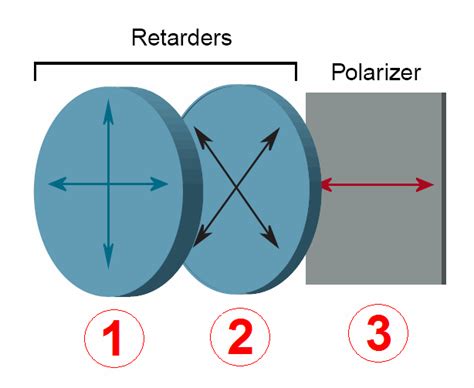
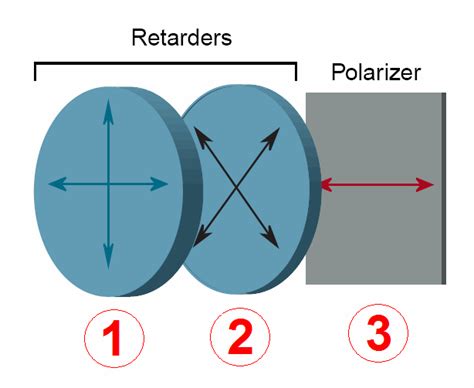
polarizers and retarders outline
In a rotating analyzer system, the retarder is placed between two linear polarizers so that the input polarization bisects the retarder's birefringence axes. Linear retardance is calculated from .An analyzer is the component of a polarimeter that allows the angle of rotation of plane-polarized light to be determined. Specific rotations are normally measured at 20°C, and this property .Traditional microscopic MM imaging polarimeter adopts the structure of dual rotating retarders, and takes at least 16 images in time sequence to recover the full 4*4 MM [21, 22, 24].As a . There are two types of retarders widely used in optical polarimetry: a retarder with τ = π∕2 (or Δ = λ∕4) is called quarter wave plate (QWP), and with the τ = π (or Δ = λ∕2), .
A computer-controlled Mueller matrix polarimeter with dual rotating retarders is described. Bulk properties of optical materials are determined by controlling the input-polarization state and .After passage through the sample, one detects the modified orientation of the polarization by passing the light through another linear polarizer (called the analyzer), which can be rotated .
polarimeter is a rotatable retarder fixed polarizer (RRFP) Stokes polarimeter with a rotatable retarder, a fixed polarizer and a photodetector, which is shown in Fig. 1. Often, a quarter-wave . polarimeter is a rotatable retarder fixed polari zer (RRFP) Stokes polarimeter with a rotatable retarder, a fixed polarizer and a photodetector, which is sho wn in Fig. 1. Often, a qua rter-
A calibration method for diattenuation and retardance errors for dual rotating retarder polarimeter is presented. The main objective of this work is to compensate the errors due to imperfect retarders, intended to enhance the increment in accuracy. As any azimuthal errors have not considered, so to apply this algorithm it is necessary to align .the laser polarization. This dual-rotating retarder-polarimeter technique requires a rotating linear re-tarder on both sides of the sample to modulate the various Mueller matrix elements onto intensity varia-tions in separate modulation frequencies. The re .
A wave passing through a half-wave plate. For a half-wave plate, the relationship between L, Δn, and λ 0 is chosen so that the phase shift between polarization components is Γ = π. Now suppose a linearly polarized wave with polarization vector ^ is incident on the crystal. Let θ denote the angle between ^ and ^, where ^ is the vector along the waveplate's fast axis.A polarimeter [1] is a scientific instrument used to measure optical rotation: the angle of rotation caused by passing linearly polarized light through an optically active substance. [ 2 ] Some chemical substances are optically active, and linearly polarized (uni-directional) light will rotate either to the left (counter-clockwise) or right .Appl Opt. 2020 Jul 20;59(21):6368-6378. doi: 10.1364/AO.397482. Authors Emanuel Chironi, Claudio Iemmi
A polarimeter is an optical instrument with which one can accurately measure the angle by which the polarization of light is rotated e.g. when it passes through an optically active medium (containing chiral molecules). Operation Principle of Polarimeters. The basic operation principle of a polarimeter comprises the following:
A computer-controlled Mueller matrix polarimeter with dual rotating retarders is described, which is currently configured to operate over the 3- to 12-microm spectral region. A computer-controlled Mueller matrix polarimeter with dual rotating retarders is described. Bulk properties of optical materials are determined by controlling the input-polarization state and .The dual-rotating-retarder configuration is one of the most common forms of the Mueller matrix polarimeter. I perform an optimization of this polarimeter configuration by minimizing the condition number of the system data reduction matrix. I find the optimum retardance for the rotating retarders to be 127°. If exactly 16 intensity measurements are used for a Mueller . An automated polarimeter based on a rotating polarizer for the measurement of linear retardance independent of laser power and detector gain is demonstrated and the accuracy has been verified by blind comparisons with interferometric and modified null retardance measurement techniques. We demonstrate an automated polarimeter based on a rotating .
The dual-rotating-retarder configuration is one of the most common forms of the Mueller matrix polarimeter. I perform an optimization of this polarimeter configuration by minimizing the condition . The telephoto imaging system has a simple structure and a small field of view, so the incident angle interval of optical surfaces is small. The most common antireflection coating is a quarter-wave thick layer of MgF 2 material, which has high transmittance and weak polarization effects in a small incidence range. The polarization properties of MgF 2 coating varies with . A dual-rotating-retarder polarimeter was used to determine the six measurable observables of the first hyperpolarizability tensor. Calibration of such an instrument requires a reference sample . The rotating sample polarimeter does not require retarders. Compensation for systematic errors from polarizers with diattenuation less than one is included in the data reduction.
Request PDF | Optimization of a dual-rotating-retarder polarimeter as applied to a tunable infrared Mueller-matrix scatterometer | The value of Mueller-matrix (Mm) scatterometers lies in their .
The theoretical model for the proposed Mueller matrix polarimeter is developed and the complete implementation of the device is described, which is at least as accurate and precise as similar, but much more expensive, polarimeters.
We previously developed a Mueller matrix microscope by combining a dual-rotating-retarder device with a commercial microscope, which holds promise for pathologic diagnosis applications. In order to increase the accuracy of a polarimeter it is necessary to compensate the errors caused by some of the components used. In dual rotating retarder Mueller matrix measurement method, the systematic errors can be caused due to the retardance and diattenuation properties of the components, non-uniform rotation of retarders stage, intensity . A computer-controlled Mueller matrix polarimeter with dual rotating retarders is described. Bulk properties of optical materials are determined by controlling the input-polarization state and measuring the output-polarization state. The Mueller matrix of a sample is obtained from polarimetric measurements, and polarization properties, i.e .
Evaporation Residue Testing
Fogging Testing
In the Stokes polarimeter considered in this work, we use two liquid crystal variable retarders (LCVRs) combined with a Glan-Thompson linear polarizer. A recently developed fitting calibration . We demonstrate an automated polarimeter based on a rotating polarizer for the measurement of linear retardance independent of laser power and detector gain.
The imaging polarimeter is used to record the Stokes vector of target scene, which can derive degree of polarization (DoP), degree of linear polarization (DoLP) and angle of polarization for describing polarization properties of the scene [10,11]. . Inspired by these studies, we try to rotate retarders to remodulate the polarization .
We previously developed a Mueller matrix microscope by combining a dual-rotating-retarder device with a commercial microscope, which holds promise for pathologic diagnosis applications. In practical applications, the signals to be measured are sensitive to systematic errors, and the measurement accuracy and the instrument calibration affect the capacity to characterize the . An optimization of the dual-rotating-retarder configuration of the Mueller matrix polarimeter by minimizing the condition number of the system data reduction matrix finds the optimum retardance for the rotating retarders to be 127 degrees. Expand
Rotatable retarder fixed polarizer (RRFP) Stokes polarimeters, which employ uniformly spaced angles over 180° or 360°, are most commonly used to detect the state of polarization (SOP) of an electromagnetic (EM) wave. . Measurement errors resulted from misalignment errors of the retarder in a rotating-retarder complete Stokes polarimeter Opt .
polarizers and retarders
polarimetry solar physics
Elisa Sanches Entrem no meu grupo gratuito 👉🏻 @elisasanchesnovamente • • minhas amigas 👇🏻 @euvictoriamatosa & @euyonnagalvao • • Inscreva-se no meu site 🔞 totalmente gratuito.
how does a rotating retarder polarimeter work|polarimetry solar physics